A new supply chain attack called GhostAction has compromised 817 GitHub repositories, stealing at least 3,325 secrets including npm, PyPI, and DockerHub tokens. Researchers at GitGuardian linked the incident to malicious commits designed to harvest CI/CD credentials from open-source projects.
How the Attack Started
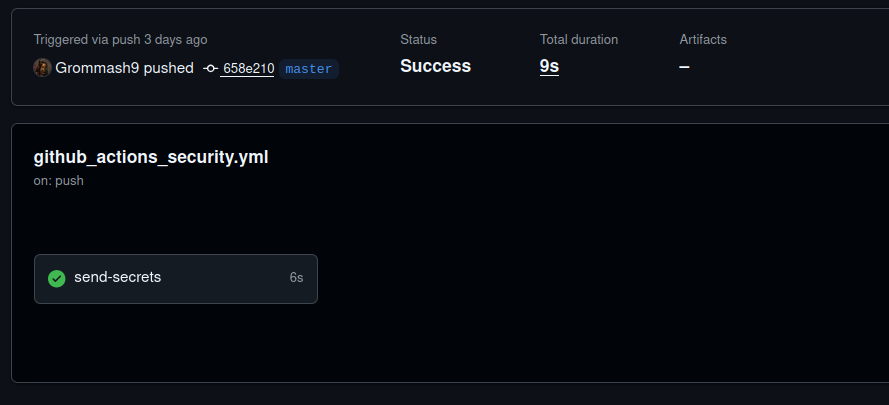
On September 2, 2025, a GitHub user operating under the handle Grommash9 committed a new workflow file to the FastUUID project, an open-source Python library for generating universally unique identifiers (UUIDs).
The file was labeled “GitHub Actions Security” and initially appeared to be a routine automation script. However, closer analysis revealed malicious code embedded within the workflow. The script was designed to collect secrets from continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines and send them to an attacker-controlled server.
Exfiltration Method
The malicious workflow contained a command that packaged authentication tokens and keys into an HTTP POST request. The stolen data was then transmitted to an external server hosted at 45.139.104.115.
Among the stolen credentials were:
- npm tokens used to publish JavaScript packages
- PyPI keys for Python package distribution
- DockerHub tokens for container image repositories
These secrets give attackers the ability to tamper with package registries, inject malicious dependencies, or hijack software supply chains.
Malicious workflow run (Source: GitGuardian)
Scope of the Breach
By September 5, 2025, GitGuardian researchers confirmed that the compromise had spread beyond FastUUID to at least 817 repositories, impacting thousands of downstream developers.
In total, 3,325 unique secrets were exfiltrated during the GhostAction campaign. Researchers warned that some of these tokens may still be valid, putting popular ecosystems at risk of secondary supply chain compromises.
GitGuardian’s Findings
GitGuardian flagged the attack as part of a growing wave of malicious GitHub Actions abuse. Since workflows often run with elevated privileges, compromised pipelines can leak high-value credentials.
“GhostAction demonstrates how attackers are embedding themselves directly into CI/CD automation,” one GitGuardian analyst explained. “This bypasses traditional defenses and exposes entire ecosystems through trusted automation scripts.”
Why GitHub Repositories Are a Target
GitHub remains the backbone of modern software development, hosting millions of open-source projects. Supply chain attacks on GitHub allow adversaries to:
- Steal developer credentials for reuse in other systems.
- Publish trojanized packages to popular registries.
- Compromise downstream organizations that rely on open-source libraries.
Because many developers automatically trust dependencies pulled from GitHub, successful attacks can quickly escalate into widespread compromises.
The GhostAction GitHub attack highlights how adversaries are targeting automation systems at the heart of software development. By compromising CI/CD workflows, attackers gain direct access to secrets that can propagate across entire ecosystems.
For open-source maintainers, the incident is a stark reminder of the risks tied to workflow automation. For enterprises, it illustrates how a single compromised repository can cascade into widespread supply chain threats.
As GitHub continues to scale, experts warn that workflow-based supply chain attacks like GhostAction will become a recurring trend unless stronger safeguards and auditing measures are enforced.





